11 Hours
Private Tour
English
UP TO 14 GUESTS
Ancient Olympia Private Day Tour
Got a Question?
Contact UsHighlights

Ancient Olympia Private tour
- Corinth Canal
- Ancient Olympia
- Archaeological Museum of Olympia
- Archaeological Site of Olympia
Itinerary
This small Peloponnese tour is a good opportunity to see the birthplace of the Olympic Games and the countryside of the Peloponnese peninsula just in one day. Beginning with a drive along the coast, you will get the chance to see some Greek seaside villages and the island of Salamis. Salamis is where the historical naval battle took place between the Athenians and the Persians.
 Our first stop of the day, the Corinth Canal. Eventually opened in 1892 separating the Peloponnese from the rest of Greece all the while connecting the Saronic Gulf to the Corinthian Sea. Having time to walk across on a pedestrian bridge and admire the canal closer.
Our first stop of the day, the Corinth Canal. Eventually opened in 1892 separating the Peloponnese from the rest of Greece all the while connecting the Saronic Gulf to the Corinthian Sea. Having time to walk across on a pedestrian bridge and admire the canal closer.
 Continuing we will drive to Ancient Olympia, passing through highways, and local streets providing you with a view of the Ionian Sea from the western coast.
Continuing we will drive to Ancient Olympia, passing through highways, and local streets providing you with a view of the Ionian Sea from the western coast.
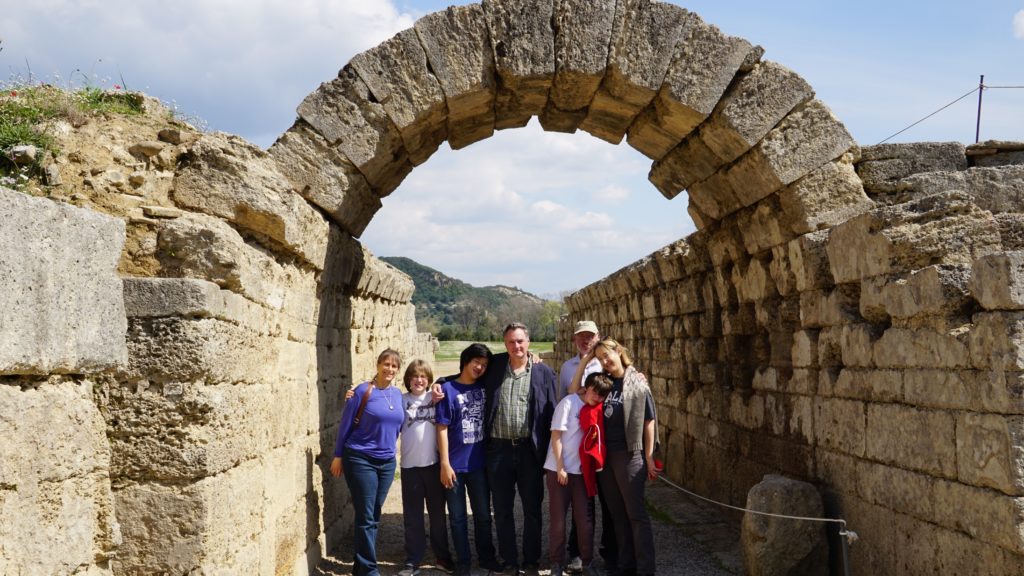
 Reaching the village at Ancient Olympia one of the largest sites in Greece, the birthplace of the Olympic Games and the Sanctuary of Olympian Zeus. Walking through the site you will pass by the Gymnasium, the Palaestra, the workshop of Phidias, the Temple of Zeus and you will end up at the Stadium where for every four years the Greeks competed for glory and for spiritual elevation honoring their cities.
Reaching the village at Ancient Olympia one of the largest sites in Greece, the birthplace of the Olympic Games and the Sanctuary of Olympian Zeus. Walking through the site you will pass by the Gymnasium, the Palaestra, the workshop of Phidias, the Temple of Zeus and you will end up at the Stadium where for every four years the Greeks competed for glory and for spiritual elevation honoring their cities.
Inclusions - Exclusions
Private Tours are personal and flexible just for you and your party.
Inclusions:
-
Professional Drivers with Deep knowledge of history [Not licensed to accompany you in any site]
-
Hotel pickup and drop-off
-
Transport by private vehicle
- Bottled water
Exclusions:
- Licensed Tour guide upon request depending on availability [Additional cost – 390 €]
- Entrance Fees [20€ for over 18 yo for Non-EU & 25 yo for EU Citizens]
- Airport Pick Up and drop-off (Additional cost)
- Food & Drinks
Entrance Fees
ADMISSION FEES FOR SITES:
Summer Period: 20€ per person
(1 April – 31 October)
Ancient Olympia: 20€ (08:00am- 20:00pm)
Winter Period: 20€ per person
(1 November – 31 March)
Ancient Olympia: 20€ (08:00am- 15:00pm)
Free admission days:
- 6 March (in memory of Melina Mercouri)
- 18 April (International Monuments Day)
- 18 May (International Museums Day)
- The last weekend of September annually (European Heritage Days)
- Every first and third Sunday from November 1st to March 31st
- 28 October
Holidays:
- 1 January: closed
- 25 March: closed
- 1 May: closed
- Easter Sunday: closed
- 25 December: closed
- 26 December: closed
Free admission for:
- Children & young people up to the age of 25 from EU Member- States
- Children & young people from up to the age of 18 from Non- European Union countries
- Persons over 25 years, being in secondary education & vocational schools from EU Member- States
- Escorting teachers during the visits of schools & institutions of Primary, Secondary & Tertiary education from EU Member- States
- People entitled to Social Solidarity income & members depending on them
- Persons with disabilities & one escort (only in the case of 67% disability)
- Refugees
- Official guests of the Greek State
- Members of ICOM & ICOMOS
- Members of societies & Associations of friends of State Museums & Archaeological sites
- Scientists licensed for photographing, studying, designing or publishing antiquities
- Journalists
- Holders of a 3- year Free Entry Pass
Reduced admission for:
- Senior citizens over 65 from Greece or other EU member-states, during
the period from 1st of October to 31st of May - Parents accompanying primary education schools visits from EU Member- States
- Escorting teachers of educational visits of schools & institutions of primary, secondary & tertiary education from non European Union countries
Reduced & free entrance only upon presentation of the required documents
History
Corinth Canal:
The famous Corinth Canal connects the Gulf of Corinth with the Saronic Gulf in the Aegean Sea. It cuts through the narrow Isthmus of Corinth and separates the Peloponnesian peninsula from the Greek mainland, thus effectively making the former an island. The canal is 6.4 kilometers in length and only 21.3 meters wide at its base. Earth cliffs flanking either side of the canal reach a maximum height of 63 meters. Aside from a few modest-sized cruise ships, the Corinth Canal is unserviceable to most modern ships. The Corinth Canal, though only completed in the late 19th  century, was an idea and dream that dates back over 2000 thousand years.
century, was an idea and dream that dates back over 2000 thousand years.
Before it was built, ships sailing between the Aegean and Adriatic had to circumnavigate the Peloponnese adding about 185 nautical miles to their journey. The first to decide to dig the Corinth Canal was Periander, the tyrant of Corinth (602 BCE). Such a giant project was above the technical capabilities of ancient times so Periander carried out another great project, the diolkós, a stone road, on which the ships were transferred on wheeled platforms from one sea to the other. Dimitrios Poliorkitis, king of Macedon (c. 300 BCE), was the second who tried, but his engineers insisted that if the seas where connected, the more northerly Adriatic, mistakenly thought to be higher, would flood the more southern Aegean. At the time, it was also thought that Poseidon, the god of the sea, opposed joining the Aegean and the Adriatic. The same fear also stopped Julius Caesar and Emperors Hadrian and Caligula. The most serious try was that of Emperor Nero (67 CE). He had 6,000 slaves for the job. He started the work himself, digging with a golden hoe, while music was played. However, he was killed before the work could be completed.
In the modern era, the first who thought seriously to carry out the project was Kapodistrias (c. 1830), the first governor of Greece after the liberation from the Ottoman Turks. But the budget, estimated at 40 million French francs, was too much for the Greek state. Finally, in 1869, the Parliament authorized the Government to grant a private company (Austrian General Etienne Tyrr) the privilege to construct the Canal of Corinth. Work began on Mar 29, 1882, but Tyrr’s capital of 30 million francs proved to be insufficient. The work was restarted in 1890, by a new Greek company (Andreas Syggros), with a capital of 5 million francs. The job was finally completed and regular use of the Canal started on Oct 28, 1893. Due to the canal’s narrowness, navigational problems and periodic closures to repair landslips from its steep walls, it failed to attract the level of traffic anticipated by its operators. It is now used mainly for tourist traffic. The bridge above is perfect for bungee jumping.
Ancient Olympia:
The history of Olympia is strongly connected to the Olympic Games. Historical records indicate that the games began in 776 BCE as a local festival to honor god Zeus. However, along the ![]() centuries, these games gained more and more popularity and all city-states of Greece would send their finest men to participate in the games. This event was so important for the ancient world that even all warfare would stop for a month so that the towns would send their best youths to participate in the games. This athletic festival occurred every four years and lasted for five days, including wrestling, chariot and horse racing, the pentathlon (discus throwing, javelin throwing, long jump, running and pancratium).
centuries, these games gained more and more popularity and all city-states of Greece would send their finest men to participate in the games. This event was so important for the ancient world that even all warfare would stop for a month so that the towns would send their best youths to participate in the games. This athletic festival occurred every four years and lasted for five days, including wrestling, chariot and horse racing, the pentathlon (discus throwing, javelin throwing, long jump, running and pancratium).
However, the athletes would stay for 1 or 2 months before the games in Olympia to train in the Palaestra. Before the games, the high priestess of Olympia marked the beginning of the games lighting the Olympic flame. Also, offerings and ceremonies in the temple of Zeus and the temple of Hera were practiced to ask for the favor of the gods. The games would take place in the stadium and people would watch them from the hills around it. All athletes were male and would take part in the games in total nudity. Women were forbidden under the penalty of death to part take in the games or even watch them as a spectator. The only woman who could watch the games, and in fact from a privileged spot, was the priestess of the temple of Demeter in Olympia.
There were no seats for the spectators and all people regardless of their social state would sit on the ground. The Hellanodikae, a body of priests, were responsible to name the winners. The reward of the winning athletes was a crown made from a wild olive tree, which was enough to honor him, his family and his city for decades. In fact, it was such an honor to be an Olympic winner that their town even pulled down a part of their city walls, as the town would be protected by the winner. At the same time, the political personalities from different parts of Greece took advantage of the games to make speeches and try to resolve differences against each other. The games were also a good opportunity for traders to make business deals. Unfortunately, in 393 AD, the Olympic Games were suspended by the Byzantine Emperor Theodosius, as it was considered a pagan custom. It was the time when Christianity was the dominant religion of the Byzantine Empire and everything connected to the ancient Greek spirit was considered pagan. Thus the games were stopped, the temples of Olympia were turned into churches and important statues, among which the golden statue of Zeus, a miracle of the ancient world, was transferred to Constantinople.
advantage of the games to make speeches and try to resolve differences against each other. The games were also a good opportunity for traders to make business deals. Unfortunately, in 393 AD, the Olympic Games were suspended by the Byzantine Emperor Theodosius, as it was considered a pagan custom. It was the time when Christianity was the dominant religion of the Byzantine Empire and everything connected to the ancient Greek spirit was considered pagan. Thus the games were stopped, the temples of Olympia were turned into churches and important statues, among which the golden statue of Zeus, a miracle of the ancient world, was transferred to Constantinople.
The revival of the Olympic Games in the modern era was an idea of the French Baron Pierre de Coubertin, who founded the International Olympic Committee in 1894 and only two years later, in 1896, the first modern Olympic Games took place in Athens, at the renovated Panathenaic Stadium. Since then, the games take place every 4 years in a different place in the world every time.
Cancellation Policy

All cancellations must be confirmed by Olive Sea Travel.
Regarding the Day Tours:
Cancellations up to 24 hours before your service date are 100% refundable.
Cancellation Policy:
- Licensed Tour Guides and Hotels are external co-operators & they have their own cancellation policy.
- Apart from the above cancellation limits, NO refunds will be made. If though, you fail to make your appointment for reasons that are out of your hands, that would be, in connection with the operation of your airline or cruise ship or strikes, extreme weather conditions or mechanical failure, you will be refunded 100% of the paid amount.
- If your cancellation date is over TWO (2) months away from your reservation date, It has been known for third-party providers such as credit card companies, PayPal, etc. to charge a levy fee usually somewhere between 2-4%.
- Olive Sea Travel reserves the right to cancel your booking at any time, when reasons beyond our control arise, such as strikes, prevailing weather conditions, mechanical failures, etc. occur. In this unfortunate case, you shall be immediately notified via the email address you used when making your reservation and your payment WILL be refunded 100%.
Frequently bought together










