11 Hours
Private Tour
English
UP TO 14 GUESTS
Mycenae-Epidaurus-Corinth & Nafplio Private Day Tour
Got a Question?
Contact UsHighlights
Ancient Greek mythology private tour
- Corinth Canal
- Ancient Corinth – Temple of Apollo
- Mycenae
- The picturesque town of Nafplio
- Palamidi – Bourtzi
- Epidaurus
Itinerary
This tour is the best way to visit numerous ancient and historical sites while also getting a taste of the Greek countryside in a single day. During the drive along the coast, you will get a view of some Greek seaside villages and the island of Salamis (where the historical battle between the Athenians and Persians took place in 480 BCE).
 The Corinth Canal will be our first stop. Finally opened in 1892, it separates the Peloponnese Peninsula from the rest of Greece and connects the Saronic Gulf to the Corinthian Sea.
The Corinth Canal will be our first stop. Finally opened in 1892, it separates the Peloponnese Peninsula from the rest of Greece and connects the Saronic Gulf to the Corinthian Sea.
Take the time to walk across on the pedestrian bridge to admire the canal closer, for the adventurous on some days bungee jumping, is an option.
 Moving on we will make our way to Ancient Corinth.
Moving on we will make our way to Ancient Corinth.
This ancient city was dominated by the Hill of Acrocorinth, the old Castle, the biggest and oldest castle in southern Greece.
 Ancient Corinth is located at the foot of the hill and includes the Roman Agora of Corinth, the Temple of God Apollo and a small museum. In addition to its archaeological and historical interest Ancient Corinth is also one of the most popular religious destinations in Greece. This was where the Apostle Paul preached Christianity, was judged by the tribunal in the Agora and established the best organized Christian church of that period.
Ancient Corinth is located at the foot of the hill and includes the Roman Agora of Corinth, the Temple of God Apollo and a small museum. In addition to its archaeological and historical interest Ancient Corinth is also one of the most popular religious destinations in Greece. This was where the Apostle Paul preached Christianity, was judged by the tribunal in the Agora and established the best organized Christian church of that period.
 Then we will be off to the Site of Mycenae dated to the 2nd millennium B.C.E. representing the era of Achilles, Agamemnon and Helen of Troy. At the site, you will see the renowned Lions Gate (the oldest architectural sculpture in Europe), the cyclopean walls, the burial circle A and the remains of Agamemnon’s Palace. Within the site, there is a modern museum exhibiting the findings of the “City οf Gold”. Before leaving the site we will make a small stop at the treasury of Atreus, the best-preserved Tholos tomb and one of the finest examples of the Mycenaean architecture.
Then we will be off to the Site of Mycenae dated to the 2nd millennium B.C.E. representing the era of Achilles, Agamemnon and Helen of Troy. At the site, you will see the renowned Lions Gate (the oldest architectural sculpture in Europe), the cyclopean walls, the burial circle A and the remains of Agamemnon’s Palace. Within the site, there is a modern museum exhibiting the findings of the “City οf Gold”. Before leaving the site we will make a small stop at the treasury of Atreus, the best-preserved Tholos tomb and one of the finest examples of the Mycenaean architecture.
 Continuing our travels we will head towards a more recent history of Greece, discovering the city of Nafplion. The city is considered the most scenic and functioned as the capital of Greece until 1834. Nafplion offers you an outstanding combination of fortresses and castles (Palamidi, Bourtzi), a huge port opened to the Aegean Sea and the unique architecture of the old city of Nafplion revealing Venetian, neoclassical and oriental elements. After walking in the idyllic place we will stop for lunch at a traditional tavern by the sea then drive up to the castle of Acronafplia for a panoramic view of the city and its surroundings.
Continuing our travels we will head towards a more recent history of Greece, discovering the city of Nafplion. The city is considered the most scenic and functioned as the capital of Greece until 1834. Nafplion offers you an outstanding combination of fortresses and castles (Palamidi, Bourtzi), a huge port opened to the Aegean Sea and the unique architecture of the old city of Nafplion revealing Venetian, neoclassical and oriental elements. After walking in the idyllic place we will stop for lunch at a traditional tavern by the sea then drive up to the castle of Acronafplia for a panoramic view of the city and its surroundings.
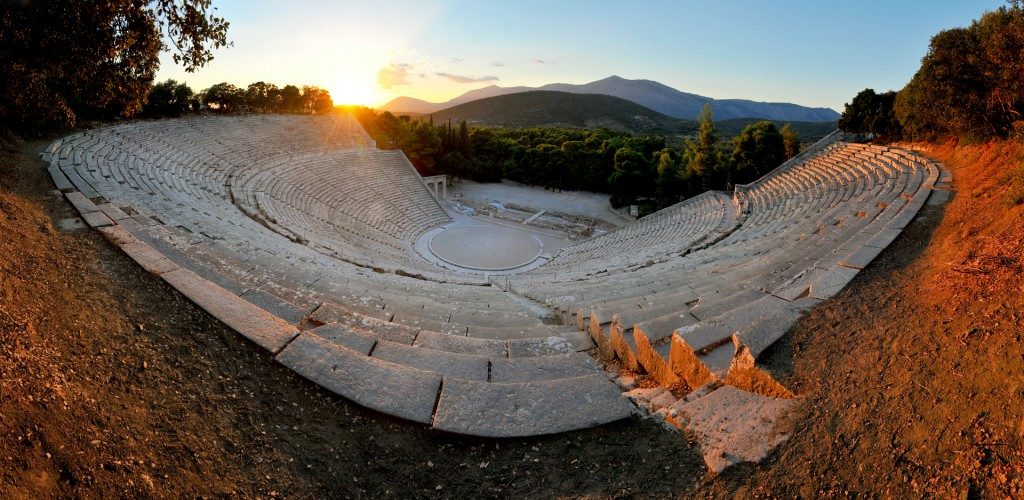
 Our last stop will be the site of Epidaurus. After a short drive, you will be able to visit one of the most important ancient Greek sanctuaries dedicated to Asclepius, the God of healing and medicine. Located in a peaceful environment and spread on a hilly area, it reaches its highest point which is the theater of Epidaurus. The best preserved ancient Greek theater dated 4th century B.C.E. proof of what miracles the ancient Greek minds could create. You can test the acoustics, great even today and climb up until the upper seats just to close your eyes and dream you attended an ancient Greek tragedy. Lastly on the way back will follow the eastern coast of Peloponnese peninsula to reach Athens again.
Our last stop will be the site of Epidaurus. After a short drive, you will be able to visit one of the most important ancient Greek sanctuaries dedicated to Asclepius, the God of healing and medicine. Located in a peaceful environment and spread on a hilly area, it reaches its highest point which is the theater of Epidaurus. The best preserved ancient Greek theater dated 4th century B.C.E. proof of what miracles the ancient Greek minds could create. You can test the acoustics, great even today and climb up until the upper seats just to close your eyes and dream you attended an ancient Greek tragedy. Lastly on the way back will follow the eastern coast of Peloponnese peninsula to reach Athens again.
Inclusions - Exclusions
Private Tours are personal and flexible just for you and your party.
Inclusions:
-
Professional Drivers with Deep knowledge of history [Not licensed to accompany you in any site]
-
Hotel pickup and drop-off
-
Transport by private vehicle
- Bottled water
Exclusions:
- Entrance Fees [32€ for over 6 yo for Non EU & 24 yo for EU Citizens]
- Licensed Tour guide upon request depending on availability [Additional cost – 330 €]
- Airport Pick Up and drop-off (Additional cost)
- Food & Drinks
Entrance Fees
ADMISSION FEES FOR SITES:
Summer Period: 32€ per person
(1 April – 31 October)
Ancient Corinth: 8€ (08:00am- 20:00pm)
Mycenae: 12€ (08:00am -20:00pm)
Epidaurus: 12€ (08:00am -20:00pm)
Winter Period: 16€ per person
(1 November – 31 March)
Ancient Corinth: 4€ (08:00am- 15:30pm)
Mycenae: 6€ (08:00am -15:30pm)
Epidaurus: 6€ (08:00am -15:30pm)
Free admission days:
- 6 March (in memory of Melina Mercouri)
- 18 April (International Monuments Day)
- 18 May (International Museums Day)
- The last weekend of September annually (European Heritage Days)
- Every first Sunday from November 1st to March 3rd
- 28 October
Holidays:
- 1 January: closed
- 25 March: closed
- 1 May: closed
- Easter Sunday: closed
- 25 December: closed
- 26 December: closed
Free admission for:
- Escorting teachers during the visits of schools and institutions of Primary, Secondary and Tertiary education and of military schools.
- Members of Societies and Associations of Friends of Museums and Archaeological Sites throughout Greece with the demonstration of certified membership card
- Members of the ICOM-ICOMOS
- Persons possessing a free admission card
- The employees of the Hellenic Ministry of Culture and Sports and the Archaeological Receipts Fund, upon presentation of their service ID card.
- The official guests of the Greek government, with the approval of the General Director of Antiquities.
- Young people, under the age of 18, after demonstrating the Identity Card or passport to confirm the age.
Reduced admission for:
- Greek citizens and citizens of other Member – States of the European Union who are over 65 years old, upon presentation of their ID card or passport for verification of their age and country of origin.
- Holders of a solidarity card
- Holders of a valid unemployment card.
- Large families’ parents of children up to 23 yrs old, or up to 25 yrs old (on military service/studying), or child with disabilities regardless the age, having a certified pass of large families, certification from the Large Family Association or a family status certificate issued by the Municipality
- Persons with disabilities (67 % or over) and one escort, upon presentation of the certification of disability issued by the Ministry of Health or a medical certification from a public hospital, where the disability and the percentage of disability are clearly stated.
- Single-parent families with minors, upon presentation of a family status certificate issued by the Municipality. In the case of divorced parents, only the parent holding custody of the children
- The police officers of the Department of Antiquity Smuggling of the Directorate of Security
- Tourist guides upon presentation of their professional ID card.
- University students and students at Technological Educational Institutes or equivalent schools from countries outside the EU by showing their student ID.
History
Corinth Canal:
The famous Corinth Canal connects the Gulf of Corinth with the Saronic Gulf in the Aegean Sea. It cuts through the narrow Isthmus of Corinth and separates the Peloponnesian peninsula from the Greek mainland, thus effectively making the former an island. The canal is 6.4 kilometers in length and only 21.3 meters wide at its base. Earth cliffs flanking either side of the canal reach a maximum height of 63 meters. Aside from a few modest-sized cruise ships, the Corinth Canal is unserviceable to most modern ships. The Corinth Canal, though only completed in the late 19th century, was an idea and dream that dates back over 2000 thousand years.
Before it was built, ships sailing between the Aegean and Adriatic had to circumnavigate the Peloponnese adding about 185 nautical miles to their journey. The first who decided to dig the Corinth Canal was Periander, the tyrant of Corinth (602 BCE). Such a giant project was above the technical capabilities of ancient times so Periander carried out another great project, the diolkós, a stone road on which the ships were transferred on wheeled platforms from one sea to the other. Dimitrios Poliorkitis, king of Macedon (c. 300 BCE), was the second who tried, but his engineers insisted that if the seas where connected, the more northerly Adriatic, mistakenly thought to be higher, would flood the more southern Aegean. At the time, it was also thought that Poseidon, god of the sea, opposed joining the Aegean and the Adriatic. The same fear also stopped Julius Caesar and Emperors Hadrian and Caligula. The most serious try was that of Emperor Nero (67 CE). He had 6,000 slaves for the job. He started the work himself, digging with a golden hoe while music was played. However, he was killed before the work could be completed.
In the modern era, the first who thought seriously to carry out the project was Kapodistrias (c. 1830), first governor of Greece after the liberation from the Ottoman Turks. But the budget, estimated at 40 million French francs, was too much for the Greek state. Finally, in 1869, the Parliament authorized the Government to grant a private company (Austrian General Etiene Tyrr) the privilege to construct the Canal of Corinth. Work began on Mar 29, 1882, but Tyrr’s capital of 30 million francs proved to be insufficient. The work was restarted in 1890, by a new Greek company (Andreas Syggros), with a capital of 5 million francs. The job was finally completed and regular use of the Canal started on Oct 28, 1893. Due to the canal’s narrowness, navigational problems and periodic closures to repair landslips from its steep walls, it failed to attract the level of traffic anticipated by its operators. It is now used mainly for tourist traffic. The bridge above is perfect for bungee jumping.
Ancient Corinth:
Located close to the isthmus which connects mainland Greece with the Peloponnese, surrounded by fertile plains and blessed with natural springs, Corinth was an important city in Greek, Hellenistic and Roman times. Its geographical location helped it play a role as a center of trade, naval fleet, participation in various Greek wars and status as a major Roman colony meant the city was, for over a millennium, rarely out of the limelight in the ancient world.
CORINTH IN MYTHOLOGY
Not being a major Mycenaean center, Corinth lacks the mythological heritage of other Greek city-states. Nevertheless, the mythical founder of the city was believed to have been King Sisyphus, famed for his punishment in Hades where he was made to forever roll a large boulder up a hill. Sisyphus was succeeded by his son Glaucus and his grandson Bellerophon, whose winged-horse Pegasus became a symbol of the city and a feature of Corinthian coins. Corinth is also the setting for several other episodes from Greek mythology such as Theseus’ hunt for the wild boar, Jason settled there with Medea after his adventures looking for the Golden Fleece and there is the myth of Arion – the real-life and gifted kithara player and resident of Corinth – who was rescued by dolphins after being abducted by pirates.
HISTORICAL OVERVIEW
The city was first inhabited in the Neolithic period (c. 5000 BCE) but became more densely populated from the 10th century BCE. The historical founders were the aristocratic descendants of King Bacchis, the Bacchiadae (c. 750 BCE). The Bacchiadae ruled as a body of 200 until in 657 BCE when the popular tyrant Cypselus took control of the city to be succeeded by his son Periander (627-587 BCE). Cypselus funded the building of a treasury at Delphi and set up new colonies.
From the 8th century BCE, Corinthian pottery was exported across Greece. With its innovative figure decoration, it dominated the Greek pottery market until the 6th century BCE when Attic black-figure pottery took over as the dominant style. Other significant exports were Corinthian stone and bronze wares. Corinth also became the hub of trade through the diolkos. This was a stone track with carved grooves for wheeled wagons which offered a land short-cut between the two seas and probably dates to the reign of Periander. In the Peloponnesian War, the diolkos was even used to transport triremes. Although the idea for a canal across the isthmus was first considered in the 7th century BCE and various Roman Emperors from Julius Caesar to Hadrian began surveys, it was Nero who actually began the project (67 CE). However, on the emperor’s death, the project was abandoned, not to be resumed until 1881.
From the early 6th century BCE, Corinth administered the PanHellenic games at nearby Isthmia, held every two years in the spring. These games were established in honor of Poseidon and were particularly famous for their horse and chariot races.
An oligarchy, consisting of a council of 80, gained power in Corinth (585 BCE). Concerned with the local rival, Argos, from 550 BCE Corinth became an ally of Sparta. During Cleomenes’ reign though, the city became wary of the growing power of Sparta and opposed Spartan intervention in Athens. Corinth also fought in the Persian Wars against the invading forces of Xerxes which threatened the autonomy of all of Greece.
Corinth suffered badly in the First Peloponnesian War, which it was responsible for after attacking Megara. Later it was also guilty of causing the Second Peloponnesian War in 433 BCE. Once again though, the Corinthians, mainly as Sparta’s naval ally, had a disastrous war. Disillusioned with Sparta and concerned over Spartan expansion in Greece and Asia Minor, Corinth formed an alliance with Argos, Boeotia, Thebes and Athens to fight Sparta in the Corinthian Wars (395-386 BCE). The conflict was largely fought at sea and on Corinthian territory and was yet another costly endeavor for the citizens of Corinth.
Corinth became the seat of the Corinthian League, but losing a war against Philip II of Macedon (338 BCE) this ‘honor’ was a Macedonian garrison being stationed on the Acrocorinth acropolis overlooking the city.
overlooking the city.
A succession of Hellenistic kings took control of the city – starting with Ptolemy I and ending with Aratus in 243 BCE when Corinth joined the Achaean League. However, the worst was yet to come when the Roman commander Lucius Mummius destroyed the city (146 BCE).
A brighter period was when Julius Caesar took charge (in 44 BCE) and organized the agricultural land into organized plots (centuriation) for distribution to Roman settlers. The city once more flourished, by the 1st century CE it became an important administrative and trade center again. In addition, following St. Paul’s visit between 51 and 52 CE, Corinth became the center of early Christianity in Greece. In a public hearing, the saint had to defend himself against accusations from the city’s Jewish that his preaching undermined the Mosiac Law. The pro-consul Lucius Julius Gallio judged that Paul had not broken any Roman law and so was permitted to continue his teachings. From the 3rd century, CE Corinth began to decline and the Germanic tribes attacked the city.
THE ARCHAEOLOGICAL SITE
In Corinth, there were cults to Aphrodite (protector of the city), Apollo, Demeter Thesmophoros, Hera, Poseidon and Helios and various buildings to cult heroes, the founders of the city. In addition, there were several sacred springs, the most famous being Peirene. Unfortunately, the destruction in 146 BCE erased much of this religious past. In Roman Corinth, Aphrodite, Poseidon and Demeter did continue to be worshipped along with the Roman gods.
The site today, first excavated in 1892 CE by the Greek Archaeological Service, is dominated by the Doric peripteral Temple of Apollo (550-530 BCE), originally with 6 columns on the façades and 15 on the long sides. A particular feature of the temple is the use of monolithic columns rather than the more commonly used column drums. Seven columns remain standing today.
The majority of the other surviving buildings date from the 1st century CE in the Roman era and include a large forum, a temple to Octavia, baths, the Bema where St. Paul addressed the Corinthians, the Asklepeion temple to Asclepius and a centre of healing, fountains – including the monumental Peirine fountain complex (2nd century CE) – a propylaea, theatre, odeion, gymnasium and stoas. There are also the remains of three basilicas.
Archaeological finds at the site include many fine mosaics – notably the Dionysos mosaic – Greek and Roman sculpture – including an impressive number of busts of Roman rulers.
Acrocorinth:
The steep rock of the Acrocorinth rises to the south-west of ancient Corinth, surmounted by the fortress, also called the Acrocorinth, which was the fortified citadel of ancient and medieval Corinth and the most important fortification work in the area from antiquity until the Greek War of Independence in 1821. It is 575 m. high and its walls are a total of almost 2.000 m. in length.
The ascent to Acrocorinth – Acrocorinthos, is facilitated by a road which  climbs to a point near the lowest gate on the west side. This commanding site was fortified in ancient times and its defenses were maintained and developed during the Byzantine, Frankish, Turkish and Venetian periods. After a moat (alt. 380 m -1247 feet) constructed by the Venetians follow the first gate, built in the Frankish period (14th,c.) and the first wall 15th c. then come the second and third walls (Byzantine: on the right, in front of the third gate, a Hellenistic tower). Within the fortress we follow a path running north-east to the remains of a mosque (16th c.) and then turn south until we join a path leading up to the eastern summit, on which there once stood the famous Temple of Aphrodite, worshipped here after the Eastern fashion (views of the hills of the Peloponnese and of Isthmus).
climbs to a point near the lowest gate on the west side. This commanding site was fortified in ancient times and its defenses were maintained and developed during the Byzantine, Frankish, Turkish and Venetian periods. After a moat (alt. 380 m -1247 feet) constructed by the Venetians follow the first gate, built in the Frankish period (14th,c.) and the first wall 15th c. then come the second and third walls (Byzantine: on the right, in front of the third gate, a Hellenistic tower). Within the fortress we follow a path running north-east to the remains of a mosque (16th c.) and then turn south until we join a path leading up to the eastern summit, on which there once stood the famous Temple of Aphrodite, worshipped here after the Eastern fashion (views of the hills of the Peloponnese and of Isthmus).
Parts of roughly dressed polygonal masonry allow us to suppose that the Acrocorinth was fortified as early as the time of the Kypselid tyranny (late 7th c. – early 6th c. BC). The surviving parts of the ancient fortifications, however, which are at many points beneath the medieval enceinte, belong mainly to the 4th c. BC. In 146 BC, Mummius destroyed the fortifications of the lower city and the Acropolis. The destroyed sections were subsequently reconstructed. During the Middle Ages, the Acrocorinth was of prime importance for the defense of the entire Peloponnese and held out against the attacks of the barbarians. The Byzantines sporadically repaired the walls, especially after hostile raids (by the Slavs, Normans and others) and added new fortifications on the west side of the fortress. In 1210, after a five-year siege, the Acrocorinth was captured by Otto de la Roche and Geoffroy I Villehardouin and was incorporated in the Frankish principate of Achaea. In the middle of this century, William Villehardouin extended the fortifications of the fortress, to be followed in this by the Angevin Prince John Gravina at the beginning of the 14th.
In 1358 the Acrocorinth passed to the Florentine banker Niccolo Acciajuoli and in 1394 to Theodoros I Palaiologos despot of Mystras. Apart from a brief occupation by the Knights of Rhodes from 1400-1404, the fortress remained in Byzantine hands until 1458, when it was captured by the Ottoman Turks. The Venetians made themselves masters of the Acrocorinth from 1687 to 1715, after which it reverted once more to the Turks until the Greek Uprising of 1821.
The approach to the fortress is from the west side. The walls have an irregular shape, which was dictated by the form of the terrain and remained the same in general terms from the Classical period to modern times. Three successive zones of fortifications, with three imposing gateways, lead to the interior of the fortress. The fact that the same material was used for extensions or repairs to the walls frequently makes it difficult to distinguish the building phases or assign a date to them.
Mycenae:
Mycenae was a fortified late Bronze Age city located between two hills on the Argolis plain of the Peloponnese, Greece. The acropolis today dates from between the 14th and 13th century BCE when the Mycenaean civilization was at its peak of power, influence and artistic expression.
IN MYTHOLOGY:
In Greek mythology, the city was founded by Perseus, who gave the site its name either after his sword’s scabbard (mykes) fell to the ground and was regarded as a good omen or as he found a water spring near a mushroom (mykes). Perseus was the first king of the Perseid dynasty which ended with Eurytheus (instigator of Hercules’ famous twelve labors). The succeeding dynasty was the Atreids, whose first king, Atreus, is traditionally believed to have reigned around 1250 BCE. Atreus’ son Agamemnon is believed to have been not only king of Mycenae but of all of the Achaean Greeks and leader of their expedition to Troy to recapture Helen. In Homer’s account of the Trojan War in the Iliad, Mycenae (or Mykene) is described as a ‘well-founded citadel’, as ‘wide-wayed’ and as ‘golden Mycenae’, the latter supported by the recovery of over 15 kilograms of gold objects recovered from the shaft graves in the Acropolis.
HISTORICAL OVERVIEW:
Situated on a rocky hill (40-50 m high) commanding the surrounding plain as far as the sea 15 km away, the site of Mycenae covered 30,000 square meters and has always been known throughout history. First excavations were begun by the Archaeological Society of Athens in 1841 and then continued by the famous Heinrich Schliemann in 1876 that discovered the magnificent treasures of Grave Circle A. The archaeological excavations have shown that the city has a much older history than traditional Greek literature described.
Even though the site was inhabited since Neolithic times, it is not until 2100 BCE that the first walls, pottery finds (including imports from the Cycladic islands) and shaft graves with higher quality grave goods appear. These, collectively, suggest a greater importance and prosperity in the settlement.
Since 1600 BCE there is evidence of an elite presence on the Acropolis: high-quality pottery, wall paintings, shaft graves and an increase in the surrounding settlement with the construction of large tholos tombs. From the 14th century BCE the first large-scale palace complex is built (on three artificial terraces), so is the celebrated tholos tomb, the Treasury of Atreus, a monumental circular building with corbelled roof reaching a height of 13.5 m and 14.6 m in diameter and approached by a long walled and unroofed corridor 36 m long and 6 m wide. Fortification walls, of large roughly worked stone blocks, surrounding the Acropolis (of which the north wall is still visible today), flood management structures such as dams, roads, Linear B tablets and an increase in pottery imports (fitting well with theories of contemporary Mycenaean expansion in the Aegean) illustrate the culture was at its zenith.
ARCHITECTURE:
The large palace structure built around a central hall or Megaron is typical of Mycenaean palaces. Other features included a secondary hall, many private rooms and a workshop complex. Decorated stonework and frescoes and a monumental entrance, the Lion Gate (a 3 m x 3 m square doorway with an 18-ton lintel topped by two 3 m high heraldic lions and a column altar) added to the overall splendor of the complex. The relationship between the palace and the surrounding settlement and between Mycenae and other towns in the Peloponnese is much discussed by scholars. The concrete archaeological evidence is lacking but it seems likely that the palace was a center of political, religious and commercial power. Certainly, high-value grave goods, administrative tablets, pottery imports and the presence of precious materials deposits such as bronze, gold and ivory would suggest that the palace was, at the very least, the hub of a thriving trade network.
The first palace was destroyed in the late 13th century, probably by an earthquake and then (rather poorly) repaired. A monumental staircase, the North Gate, and a ramp were added to the Acropolis and the walls were extended to include the Persea spring within the fortifications. The spring was named after the city’s mythological founder and was reached by an impressive corbelled tunnel (or syrinx) with 86 steps leading down 18m to the water source. It is argued by some scholars that these architectural additions are evidence for a preoccupation with security and possible invasion. This second palace was also destroyed, this time with signs of fire. Some rebuilding did occur and pottery finds suggest a degree of prosperity returned briefly before another fire ended an occupation of the site until a brief revival in Hellenistic times. With the decline of Mycenae, Argos became the dominant power in the region. Reasons for the demise of Mycenae and the Mycenaean civilization are much debated with suggestions including natural disaster, over-population, internal social and political unrest or invasion from foreign tribes.
Epidaurus:
Located on the fertile Argolid plain of the eastern Peloponnese and blessed with a mild climate and natural springs, the sanctuary of Asclepius at Epidaurus was an important sacred center in both ancient Greek and Roman times.
Epidaurus was named after Epidauros, son of Apollo. Inhabited since Neolithic times, the first significant settlement was in the Mycenaean period. Fortifications, a theatre and tholos tombs have been excavated dating as early as the 15th century BCE, although it was in the 12th century BCE that Epidaurus Limera, with its harbor linking it to the Aegean trade network, particularly flourished.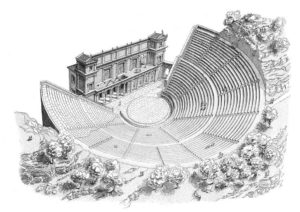
Earlier regional worship of the deity Maleatas evolved into the later worship of Apollo, who was given similar attributes. However, it was Asclepius (also spelled Asklepios), whom the Epidaurians believed was born on the nearby Mt. Titthion, who took precedence from the 5th century BCE until Roman times in the 4th century CE. Credited with possessing great healing powers (learned from his father Apollo) and also those of prophecy, the god – as manifested in the sanctuary or Asklepieion – was visited from all over Greece by those seeking ease and remedies from their illnesses either by divine intervention or medicines administered by the priests. The sanctuary used the wealth gained from dedications of the worshipers to build an impressive complex of buildings and to sponsor major art projects to beautify the center. Indeed, many of the offerings given were works of art such as statues, pottery vessels, tripods and even buildings.
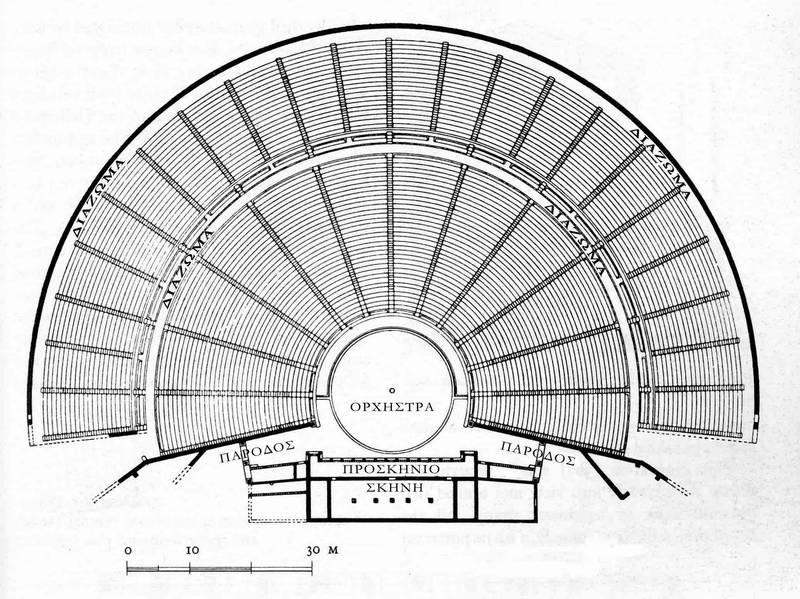
At the height of the site’s importance in the 4th century BCE (370-250 BCE), major buildings included two monumental entrances (Propylaea); a large temple (380-375 BCE) with the typical 6×11 column Doric layout, containing a larger than life-size Chryselephantine statue of a seated Asclepius (by Thrasymedes) and with pediments displaying in statuary the Amazonomachy and the Siege of Troy; temples dedicated to Aphrodite (320 BCE), Artemis and Themis; a sacred fountain; the Thymele (360-330 BCE) – a round marble building originally with 26 outer Doric columns, a 14 Corinthian columned cella and a mysterious underground labyrinth, perhaps containing snakes which were associated with Asclepius; the columned Avaton (or Enkoimeterion) in which patients waited overnight for divine intervention and remedy; other temples, hot and cold bath houses, stoas, stadium, palaistra and large gymnasia; and a 6000 seat theatre (340-330 BCE). These latter sporting and artistic buildings were used in the Asklepieia festival, founded in the 5th century BCE and held every 4 years to celebrate theatre, sport and music. The theatre, with 2nd century CE additions resulting in 55 tiers of seats and a capacity of perhaps 12,300 spectators, would become one of, if not the, largest theatres in antiquity. Other Roman additions to the site in the 2nd century included a temple of Hygieia, a large bath building and a small odeum.
The site was destroyed in 395 CE by the Goths and the Emperor Theodosius II definitively closed the site along with all other pagan sanctuaries in 426 CE. The site was abandoned once and for all following earthquakes in 522 and 551 CE. Excavations at the ancient site were first begun in 1881 CE by the Greek Archaeological Society and continue to the present day. Today, the magnificent theatre, renowned for its acoustics, is still in active use for performances in an annual traditional theatre festival.
Nafplio:
The city of Nafplio was the first capital of the modern Greek state. Named after Nafplios, son of Poseidon, and home of Palamidis, their local hero of the Trojan war and supposedly the inventor of weights and measures, lighthouses, the first Greek alphabet and the father of the Sophists. The small city-state made the mistake of allying with Sparta in the second Messenian War (685-688BC) and was destroyed by Damokratis, the king of Argos.
Because of the strength of the fort that sits above the bay, the town of Nafplio became an important strategic and commercial center to the Byzantines from around the 6th century AD. In 1203 Leon Sgouros, ruler of the city, conquered Argos and Corinth, and Larissa to the north, though it failed to successfully conquer Athens after a siege in 1204.
With the fall of Constantinople to the Turks, the Franks, with the help of the Venetians, captured the city and nearly destroyed the fortress in the process. In the treaty, the defenders of the city were given the eastern side of the city, called the Romeiko and allowed to follow their customs, while the Franks controlled the Akronafplia, which was most of the city at the time. The Franks controlled the city for 200 years and then sold it to the Venetians. The Venetians continued the fortification of the upper town and completed their work in 1470. That same year they built a fort on the small island in the center of the harbor called the Bourtzi. To close the harbor, the fort was linked by chains and the town was known as Porto Cadenza, meaning Port of Chains. During this period people flocked to the safety of the fortified city in fear of the Turks and forced the expansion of the city into the lagoon between the sea and the walls of the Akronafplia. The new additions to the city were surrounded by walls and many major buildings were erected including the Church of Saint George. But these new walls didn’t matter because in the treaty with Suleiman the First, Nafplio was handed over to the Turks who controlled the city for 100 years and made it the primary import /export center for mainland Greece.
In 1686 the Turks surrendered the city to a combined force of Venetians, Germans and Poles, led by Vice Admiral Morozini and this began the second period of Venetian rule in which massive repairs were made to the fortress and the city including the construction of the fortress in Palamidi. When the Peloponnese falls to the Venetians, Nafplio becomes the capital. But after just 30 years the Turks once again take control of the city, almost totally destroying it, looting it and killing almost all its defenders. Most of the survivors chose to leave the city while the Turks built mosques, baths and the homes in the eastern style which can still be seen.
In April of 1821 Greek chieftains and Philhellenes surrounded the city of Nafplio and liberated it from the Turks under the leadership of Theodore Kolokotronis. Nafplio became the center of activities which would result in the formation of Modern Greece. In 1823 it becomes the capital of the state which is then recognized by the world powers (England, France and Russia) in 1827. 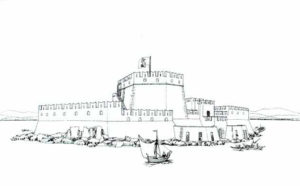
In January of 1828, Ioannis Kapodistrias is recognized as the first governor and arrives in Nafplion. In 1831 King Otto is chosen as the first King of Greece but a month later Kapodistrias is murdered in the Church of Agios Spiridon.
In 1833 King Otto arrives amid great fanfare to the city of Nafplio where he remains until 1834 when the capital of Greece is moved to Athens.
In 1862 there is a rebellion in Nafplio against the monarchy. A siege by the royal army follows. The rebels are given amnesty in 1862. In 1834 Kolokotronis is jailed in the Palamidi fortress. After the capital moves to Athens, the city of Nafplio becomes of less importance. But it still continues to attract visitors to this very day because its history is virtually the history of modern Greece and because every occupying power has left its mark.
The city of Nafplio is like a living museum. It’s also as lively as any city in Greece.
Cancellation Policy

- All cancellations must be confirmed by Olive Sea Travel.Regarding the Day Tours:
Cancellations up to 24 hours before your service date are 100% refundable.
Cancellation Policy:
- Licensed Tour Guides and Hotels are external co-operators & they have their own cancellation policy.
- Apart from the above cancellation limits, NO refunds will be made. If though, you fail to make your appointment for reasons that are out of your hands, that would be, in connection with the operation of your airline or cruise ship or strikes, extreme weather conditions or mechanical failure, you will be refunded 100% of the paid amount.
- If your cancellation date is over TWO (2) months away from your reservation date, It has been known for third-party providers such as credit card companies, PayPal, etc. to charge a levy fee usually somewhere between 2-4%.
- Olive Sea Travel reserves the right to cancel your booking at any time, when reasons beyond our control arise, such as strikes, prevailing weather conditions, mechanical failures, etc. occur. In this unfortunate case, you shall be immediately notified via the email address you used when making your reservation and your payment WILL be refunded 100%.
Recommended for you

Athens By Night Private Tour











